26.06.2025

What Words Reveal: Analyzing Language in the Trump–Harris 2024 Debate
MCML Research Insight - With Philipp Wicke
In presidential debates, every word counts - not only what candidates say but how they say it. Words are carefully selected to resonate with voters’ values, fears, and hopes. A new insightful study by MCML Junior Member Philipp Wicke and Marianna M. Bolognesi dives deep into the September 10, 2024 debate between Donald Trump and Kamala Harris.
Their central question:
Do Democratic and Republican Candidates Genuinely Differ in Their Linguistic Strategies?
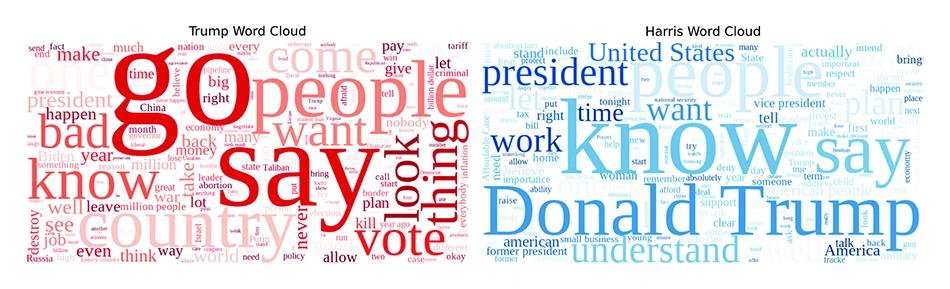
©Wicke et al.
The word cloud shows red words for Trump and blue words for Harris, with word size representing frequency, highlighting the most common terms in their responses.
Methodology: Combining AI With Human Expertise
The researchers analyzed the complete debate transcript using sophisticated natural language processing techniques and expert human annotations. They assessed emotional tone, concreteness, specificity, figurative language (like metaphors), and pronoun usage. Large language models, such as GPT-4o, were utilized to detect figurative frames, and these AI-generated results were rigorously validated by human experts, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
What Is Framing?
Framing refers to how authors shape the meaning of their messages by emphasizing certain perspectives or values - often through metaphors or emotionally charged imagery. For example, describing immigration as a “flood” frames it as a natural disaster, influencing how the audience perceives the issue.
«Trump’s figurative frames reveal distinct themes at both content and framing levels… framing the country as facing existential decline, using metaphors like ‘we’re a failing nation,’ ‘our country is being lost,’ and ‘they’re destroying our country.»
Philipp Wicke
MCML Junior Member
Key Linguistic Findings
The analysis unveiled clear rhetorical distinctions aligned with each candidate’s political identity:
- Framing the Narrative: Harris frequently utilized metaphors emphasizing growth, unity, and recovery, crafting a narrative around national progress and collective strength. Trump, conversely, painted scenarios of decline, threat, and crisis, using vivid, emotionally charged language to depict invasions, societal collapse, and betrayal.
- Emotion and Subjectivity: Both candidates employed negative emotional language, reflecting the polarized political atmosphere. Trump’s rhetoric was more negative and somewhat more “objective,” framing his opinions as facts to assert authority. Harris used language that was slightly more subjective, indicating empathy and personal conviction.
- Specificity and Concreteness: Contrary to popular expectations, both Trump and Harris exhibited similar levels of abstract versus concrete language, challenging assumptions about vagueness or excessive policy detail attributed to one side or the other.
- Pronoun Usage and Identity: Pronouns revealed notable strategies. Harris balanced “we” and “I,” highlighting collective responsibility and inclusive leadership. Trump predominantly used “I” and “me,” reinforcing personal authority and decisiveness. Additionally, Trump never directly mentioned Harris by name, while Harris frequently referred to Trump explicitly, reflecting contrasting debate tactics.
The Bigger Picture
These findings resonate with broader patterns observed in political discourse. Republican language often stresses strength, individualism, and moral urgency, whereas Democrats typically emphasize empathy, collective action, and social justice. This study not only confirms these established ideological divisions but shows how deeply they influence the fundamental structure of candidates’ communication strategies.
Want to Explore More?
The complete study, featuring in-depth analyses, visualizations, and full datasets, is published in the renowned PLOS One journal and freely available. Examine the data or explore the underlying code to discover the strategic language choices that influence political debates. Gain insight into the language of leadership and how it influences political reality or apply the tools to analyze a different debate entirely. While the 2024 debate is now part of the past, the code remains highly relevant and easily adaptable for examining future political showdowns between two candidates.
Red and blue language: Word choices in the Trump and Harris 2024 presidential debate.
PLOS One 20.6. Jun. 2025. DOI GitHub
Share Your Research!
Get in touch with us!
Are you an MCML Junior Member and interested in showcasing your research on our blog?
We’re happy to feature your work—get in touch with us to present your paper.
Related

24.02.2026
Cosmology: Measuring the Expansion of the Universe With Cosmic Fireworks
Daniel Gruen leads LMU’s campaign on rare SN Winny to refine the Hubble constant and address the Hubble tension in cosmology.

19.02.2026
COSMOS – Teaching Vision-Language Models to Look Beyond the Obvious
Presented at CVPR 2025, COSMOS shows how smarter training helps VLMs learn from details and context, improving AI understanding without larger models.

05.02.2026
Daniel Rückert and Fabian Theis Awarded Google.org AI for Science Grant
Daniel Rueckert and Fabian Theis receive Google.org AI funding to develop multiscale AI models for biomedical disease simulation.

